Zero Trust is a security strategy and framework that follows the principle “Never Trust, Always Verify”.
It assumes that the request, user or device is not secured and should not be trusted by default, no matter if it is inside or outside organization’s network perimeter. Zero Trust model continuously authenticate users and devices (instead of just once), encrypt everything, provide the minimum access needed and limit access duration, and use segmentation to limit the damage of any breaches. It is a holistic approach to safeguard identities, endpoints, applications, network, infrastructure and data.
Table of contents
Zero Trust principles.
The Zero Trust security framework operates on key principles to provide multiple layers of defense:
- Verify explicitly: Always authenticate and authorize based on all available data points, including user identity, location, device health, service or workload, data classification, and anomalies. This ensures the constant monitoring and validating of who can access what.
- Use least-privilege access: Limit user access with just-in-time and just-enough access (JIT/JEA), risk-based adaptive polices, and data protection to help secure both data and productivity. This means only granting access to systems and applications to authorized users for specific tasks for a minimum time.
- Assume breach: Assume breach is the mindset of creating the necessary segregation of access to contain the damage to a small area, and in doing so, minimizing the impact to your business. Verify end-to-end encryption and use analytics to get visibility, drive threat detection, and improve defences.
How does Microsoft uses zero trust framework?
Most of the organization uses multicloud and Hybrid (on-premise and cloud). They may focused on the strategy to protect network access with on-premise firewalls and VPNs assuming that everything inside the network was safe. The corporate data may reside in the cloud or hybrid or across both.
In order for the user, process or app to access the data, everything including identity, app, network, device are verified and encrypted. Microsoft uses Zero Trust security layers to enforce Zero Trust framework within Microsoft products.
Microsoft’s approach for Zero Trust is not to disrupt end users, but work behind the scenes to keep users secure as they work.
Zero Trust security layers.
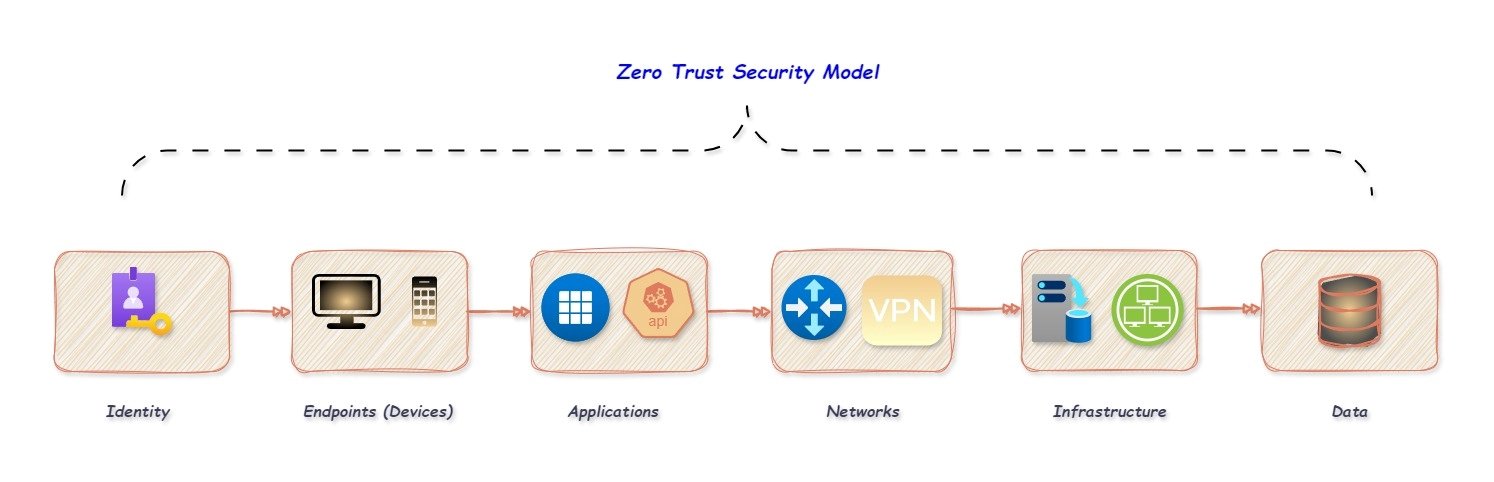
In the Zero Trust approach, identity, endpoints, applications, network, infrastructure, and data are important components that work together to provide end-to-end security. It is also known as Zero Trust security layers.
Identity.
Microsoft Entra ID can act as a unified directory service to authenticate users, devices, and processes to your resources, apps, and services, across multicloud and Hybrid (on-premise and cloud).
When a user attempts to access a data, Microsoft Entra ID will verify the credentials, two factor authentication and Conditional Access to confirm if the data can be accessed or not. It checks for real-time user and sign-in risk detections when evaluating data access requests.
Recommendations for the organization:
- Use Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps access policies enable real-time monitoring and control over access to cloud apps based on user, location, device, and app.
- Disable legacy authentication methods.
- Implement multifactor authentication (MFA).
- Use identity secure score.
- Use Identity Protection.
- Implement single sign-on (SSO)
- Enable passwordless authentication (Windows Hello, MFA, FIDO2 Key)
- Use Conditional Access policies to protect the access to the resources.
Endpoints (Devices).
Once user has been granted access to a data, the user can use different devices to access data. The device may not be owned and managed by the organization. What if the device used to access the data is not updated? it poses a great security risk of data leakage and exposure to unwanted people.
With conditional access policy, we can limit the data access to only corporate or personally-owned computers and mobile devices, we can block the data access on unmanaged device or force the device to register or join the directory service.
Using Microsoft Endpoint Manager, we can make sure that the devices and the installed apps, which access the data meet your security and compliance policy requirements of the organization regardless of whether the device is owned by your organization or the user.
Recommendations for the organization:
- Register the devices with the identity provider.
- Enable real-time device risk evaluation.
- Use mobile device management (MDM) tool.
- Make sure managed devices required to be compliant with IT configuration policies before granting access.
- Setup data loss prevention policies on all managed and unmanaged devices.
- Implement endpoint threat detection to enable real-time device risk evaluation.
Applications.
Using Applications and APIs, the user access the data. The application can be cloud application or it can be legacy application hosted on the on premises of the organization.
Microsoft Endpoint Manager can be used to configure and enforce policy management for both desktop and mobile apps, including browsers. For example, we can prevent work related data from being copied and used in personal apps.
Microsoft Cloud App Security can help us discover and manage Shadow IT services, with catalogue of more than 17,000 apps. With MCAS, the organization can block actions within a cloud app, example: downloading the files is blocked on unmanaged devices.
Recommendations for the organization:
- Enforce policy-based access controls for the applications (App protection policies for Microsoft 365 (Office) apps).
- Use conditional access session controls for the apps.
- connect business-critical apps to the cloud app security platform to monitor cloud data and cloud threats.
- Discover and manage shadow IT in your network.
Networks.
The application and the users will use a network to access the data. To enhance visibility and help prevent attackers from moving laterally across the network, organizations should segment networks.
Using network access controls and monitoring user and device behaviour in real time can provide insights and visibility into threats (ML-based threat protection and filtering with context-based signals).
Recommendations for the organization:
- Corporate network should have External firewall, Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack protection, Web application firewalls to quickly detect, respond and protect the networks from attacks.
- Encryption (using certificates or other methods) for all network traffic, whether it’s internal, inbound or outbound.
- Network Segmentation to limit the lateral movements of attacks on your network.
Infrastructure.
An infrastructure can be anything from an on-premises servers to cloud-based virtual machines.
The main focus and consideration for infrastructure is to manage the configuration and keep software updated. It should also meet the organizations security and policy requirements.
Azure Sentinel is a cloud-native security information event management (SIEM) and security orchestration automated response (SOAR) solution that will allow your Security Operations Center (SOC) to work from a single pane of glass to monitor security events across your enterprise.
Microsoft Defender for Identity enables signal collection to identify, detect, and investigate advanced threats, compromised identities, and malicious insider actions.
security orchestration, automation, and remediation (SOAR) tooling to reduce manual effort in threat response.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Advanced Threat Protection includes automated investigation and remediation capabilities to help examine alerts and take immediate action to resolve breaches.
Privileged Identity Management (PIM) in Azure AD enables you to discover, restrict, and monitor access rights for privileged identities. PIM can help ensure your admin accounts stay secure by limiting access to critical operations using just-in-time, time-bound, and role-based access control.
Recommendations for the organization:
- Enable cloud infrastructure protection solutions across your hybrid and multicloud using Azure Security Center.
- Have an app identity assigned to the workloads. Azure Active Directory supports managed identities, enabling easy access to other Azure AD-protected resources such as Azure Key Vault, where secrets and credentials are securely stored.
- Use security information and event management (SIEM) solution to aggregate and analyse events across multiple sources.
- Use behaviour analytics to detect and investigate threats using Microsoft Defender for Identity.
- Regularly review administrative privileges (at least every 180 days) to ensure admins only have just enough administrative rights.
Data.
Understanding your data and then applying the correct level of access control is essential if you want to protect it. But it goes further than that. By limiting access, and by implementing strong data usage policies, and using real-time monitoring, you can restrict or block sharing of sensitive data and files.
Recommendations for the organization:
- Data classification, rule-based and keyword methods are used to discover and classify sensitive data across some locations, apps, services.
- Access decisions governed by data sensitivity rather than simple network perimeter controls.
- Corporate data actively and continuously discovered by sensitivity in any location.
- The most sensitive files persistently protected with encryption to prevent unauthorized access use.
- Data loss prevention controls in place to monitor, alert, or restrict the flow of sensitive information (for example, blocking email, uploads, or copying to USB).
Conclusion.
At the end of the day Zero Trust is all about understanding and then applying the right controls to protect your Data. Microsoft will provide an organization the controls to limit data access only to the people and processes that need it. The policies the organization set, along with real-time monitoring, can then restrict or block the unwanted sharing of sensitive data and files. Zero Trust in the cloud encrypts anything stored in the cloud, manages access, helps identify any breaches to cloud infrastructure, and speeds up remediation.