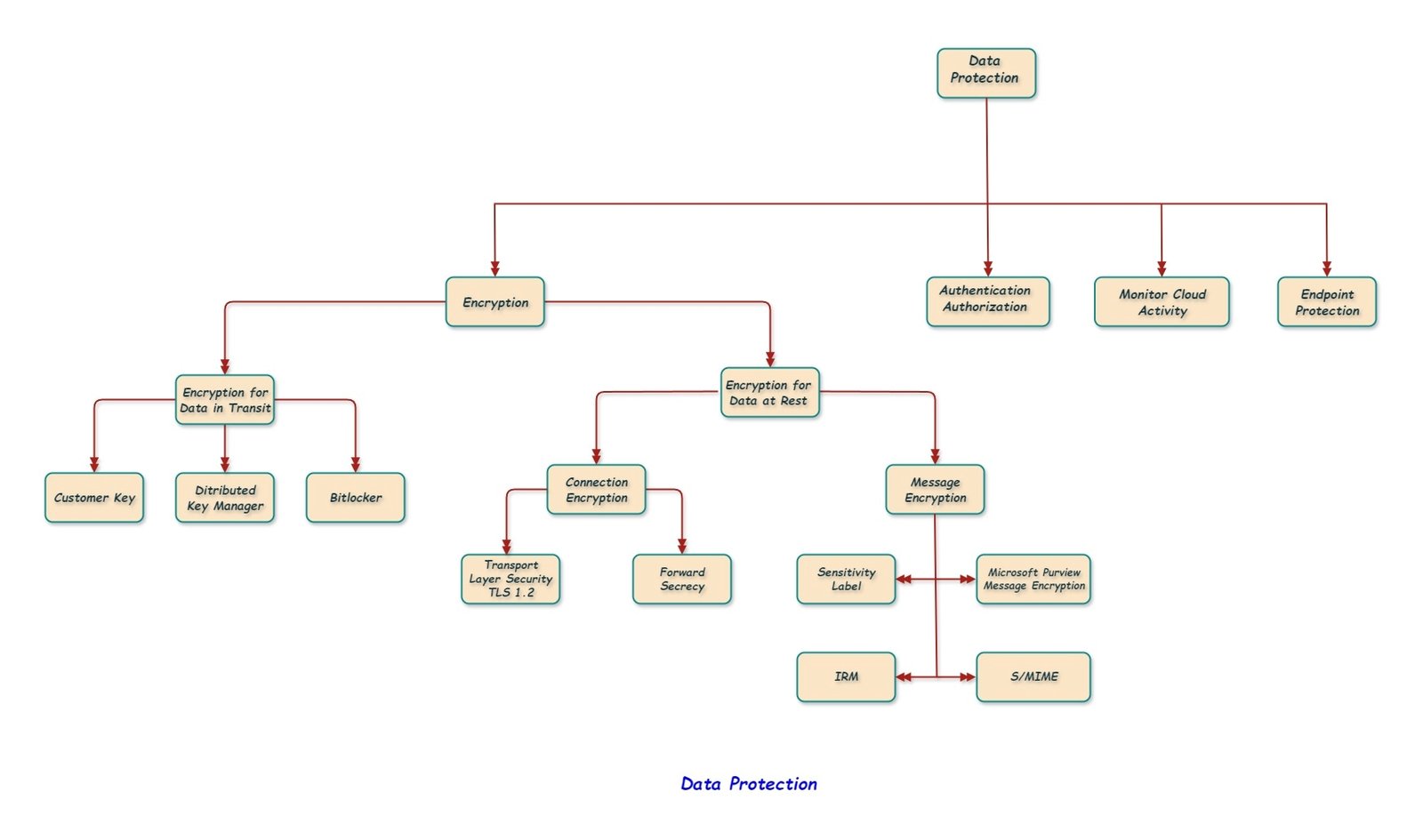
Data Protection refers to security processes that makes sure the data is safe, weather the data is stored on Microsoft 365 servers (SharePoint site, email stored in mailbox) or if the data (email, file) is moving from one server to another server within Microsoft 365 data center.
The purpose of data protection is to safeguard the organization’s data against compromise, harm, and loss. If the data is stored in the data center, then it is data at rest, If the data is moving within Microsoft data center, then it is said to be data in transit.
Microsoft 365 always encrypts the data in transit and data at rest using one or more forms of encryption for all cloud models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS).
Table of contents
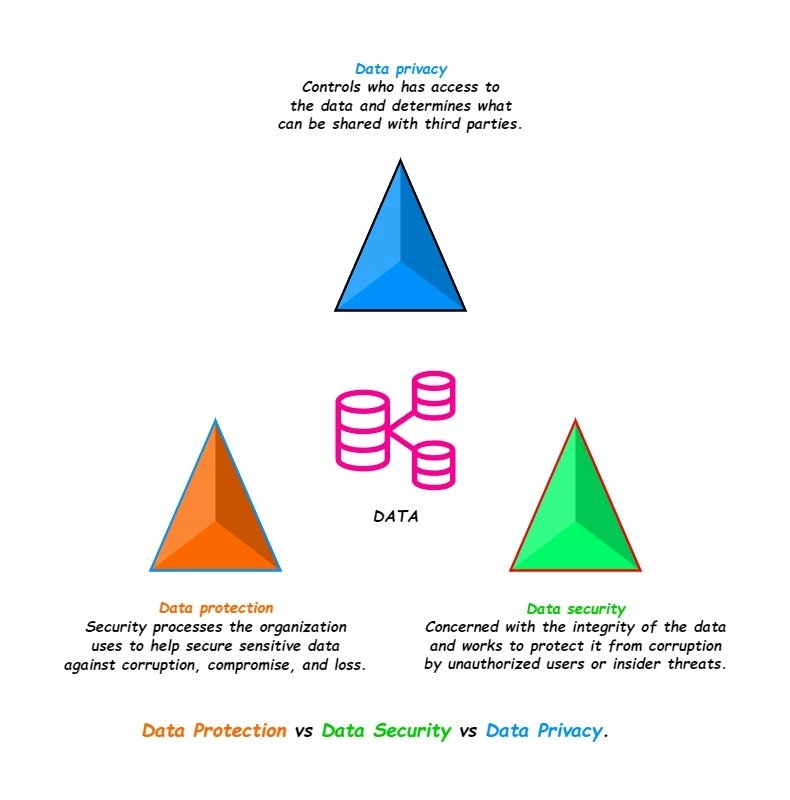
Data Protection vs Data Security vs Data Privacy.
Data protection is the security processes the organization uses to help secure sensitive data against corruption, compromise, and loss.
security of data is concerned with the integrity of the data and works to protect it from corruption by unauthorized users or insider threats.
Data privacy controls who has access to the data and determines what can be shared with third parties.
Encryption for data at rest.
Data at rest includes information that is stored on physical media, in any digital format.
Attacker may try to physically access data center to reach hard drive storing customer data. If successful he may attempt to access to the data on the hard drive.
Data at rest encryption secures unencrypted data by encrypting it on disk, preventing unauthorized access.
BitLocker.
Microsoft servers uses BitLocker to encrypt disk drives holding customer data at rest in data centers. BitLocker can also be used on client machines, such as Windows computers and tablets.
It eliminates the potential for data theft or exposure because of lost, stolen disks. BitLocker is deployed with Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) 256-bit encryption on disks containing customer data in EXO, SPO, and Teams.
BitLocker key management involves the management of recovery keys that are used to unlock/recover encrypted disks in a Microsoft data center.
Microsoft 365 stores the master keys in a secured share, only accessible by individuals who have been screened and approved.
Distributed Key Manager (DKM).
Microsoft also uses Distributed Key Manager to encrypt the data in Exchange Online data centers.
Distributed Key Manager (DKM) is a client-side technology that uses a set of secret keys to encrypt and decrypt information. Only members of a specific security group in Active Directory Domain Services can access those keys in order to decrypt the data that is encrypted by DKM.
For debugging, troubleshooting, or auditing purposes, a data center administrator must request elevated access to gain temporary credentials that are part of the security group. This process requires multiple levels of legal approval. If access is granted, all activity is logged and audited. Access is only granted for a set interval of time after which it automatically expires.
DKM is used to protect the data like Email account credentials for connected accounts or customer key.
Customer Key.
Microsoft 365 provides baseline, volume-level encryption enabled through BitLocker and Distributed Key Manager (DKM). It also offers an added layer of encryption for customer data through Customer Key.
With Customer Key, you control the organization’s encryption keys and then configure Microsoft 365 to use them to encrypt your data at rest in Microsoft’s data centers. You control the encryption keys that Microsoft 365 uses to encrypt and decrypt data.
Customer Key provides extra protection against viewing of data by unauthorized systems or personnel, and complements BitLocker disk encryption and Distributed Key Manager (DKM).
Encryption for Data in Transit.
This include mail messages that are in the process of being delivered, or conversations that are taking place in an online meeting. In Microsoft 365, data is in transit whenever a user’s device is communicating with a Microsoft server, or when a Microsoft server is communicating with another server.
Connection Encryption.
Microsoft 365 encrypts the connection for the servers in the data center for all workloads (SPO, EXO), no matter if the data enters or exits the data center. Connection encryption is achieved using the below protocols.
Transport Layer Security (TLS 1.2) or Higher.
Microsoft 365 servers always encrypt connections to other servers in the data centers with TLS 1.2. Once the connection is encrypted, all data sent through that connection is sent through the encrypted channel. When you send a message to a recipient that is within your organization, Exchange Online automatically sends the message over an encrypted connection using TLS.
TLS doesn’t encrypt the message, just the connection. When you forward a message that was sent through a TLS-encrypted connection to a recipient organization that doesn’t support TLS encryption, that message isn’t necessarily encrypted.
Forward Secrecy / Perfect Forward Secrecy.
Forward Secrecy or Perfect Forward Secrecy is an encryption method that uses temporary private key exchanges between servers and clients. PFS can be found within transport layer security (SSL/TLS).
Instead of encrypting the session using a single special key, a new session key is generated for each session, because of which the data is not compromised, and is safe from the attackers.
In case the one session key is compromised, the data from any other sessions will not be compromised because a new session key will again be generated and used each time a session is initiated.
Message Encryption.
Below are the options using which an email, message or a file is encrypted or protected.
Sensitivity Label.
It helps you to label and protect your data regardless of which device it is stored on, which application or service it is stored in, and whether it travels inside or outside your organization.
The organization can use sensitivity labels to encrypt the content of message or file, control who can access and view labeled items and add custom headers, footers, and watermarks to labeled items.
Using this feature we can control the email or file, example: block forwarding or printing of the file or message.
Sensitivity labels are created and configured by the Administrator, while it is used or applied on the email at the time of email creation.
Microsoft Purview Message Encryption.
Using Microsoft Purview Message Encryption, you can send encrypted email to people inside or outside the organization. The recipient can be hosted on Exchange online or can be hosted on Gsuite, Gmail, Yahoo, Outlook.com.
Administrator must setup transport rules to define the conditions for encryption. When the user sends the email, the admin created rule will get applied.
When the recipient tries to view the encrypted email, he can either get a one-time passcode, sign in with a Microsoft account, or sign in with a work or school account associated with Office 365.
Once the recipient uses any of the above methods, the recipient will be able to view the encrypted email. The recipient can also send a reply to the same encrypted email and the reply will also be encrypted.
Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME).
S/MIME is a certificate-based encryption solution that allows you to both encrypt and digitally sign a message. The message encryption helps ensure that only the intended recipient can open and read the message and protects the content of email messages. A digital signature helps the recipient validate the identity of the sender.
S/MIME certificate needs to be installed on the email clients of both the recipient and the sender to ensure email encryption at both ends. When an email is sent, the sender encrypts the email using the recipient’s public key and the recipient decrypts the email using the private key.
S/MIME also attaches a digital signature to an email. This ensures that the sender is authorized to send emails from a specific domain.
Information Rights Management (IRM).
Information Rights Management (IRM) helps you prevent sensitive information from being printed, forwarded, or copied by unauthorized people. It also provides online and offline protection of email messages and attachments.
It can also be used to protect the SharePoint document libraries and lists for SharePoint Online.
IRM can be used with both Exchange on-premises organization and Exchange Online.
You must activate Rights Management service (RMS) before you use Information Rights Management (IRM) features of Microsoft 365 services. After you activate RMS, your organization can start to protect important documents and emails by using Azure RMS.
Monitor cloud activity using Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a multi cloud monotiling and security solution. Monitoring cloud activity can help detect and prevent unauthorized access to data. Cloud service providers offer monitoring services that can alert administrators when suspicious activity is detected.
An organization should regularly reviewing cloud logs and audit trails can help identify potential security threats. Please refer this article to get the list of activities captured Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
Authentication and Authorization.
Authentication and authorization are the two important information security processes where as Authentication verifies the identity of a user or service which is trying to access to data, Authorization determines with what access rights the user can access the data.
Role-based access control limits access to necessary individuals, enhancing security when used with identity and access management systems.
Endpoint (Device) protection.
Endpoint refers to the physical device or virtual machine which are used by the users to access the organization resources. Example: mobile devices, desktop computers, virtual machines, embedded devices, and servers. Endpoint protection helps the organization monitor and safeguard the data which is being access by the user on the device.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint solution helps the organization to protect the endpoint from different form of cyberattacks.
Conclusion.
Protecting the customer data in cloud services is difficult due to development of new attack strategies by hackers. CSP and organizations uses various technologies to prevent unauthorized data access.
Data protection strategy includes monitoring and protecting data within the environment and maintaining continuous control over data visibility and access.
Microsoft 365 ensures the data protection using various methods explained in this article.