In this article we will take a look at types of Outbound Mail Flow scenarios an organization can setup based on the different types of exchange environment.
By default, Exchange Online Protection email sending servers will send all outbound emails to external recipients.
When an administrator adds a custom domain in Microsoft 365 tenant, the setup will ask us to add MX record, SPF record (TXT) and Autodiscover record (CNAME) for Exchange Online services.
The added TXT record will appear as (v=spf1 include:spf.protection.outlook.com -all). This implies that when sending emails to external recipients via EOP email sending servers, the SPF record check at the recipient end should pass.
The organization can also route the outbound email using a 3rd party email service (also known as Conditional mail routing or Criteria Based Routing, it uses outbound connector and transport rule) or route the email to the on premises exchange server first and then on premises server will deliver the email to the recipient server over the internet (also known as Centralized Mail Transport).
Table of contents
- Exchange Online Email Sending Pools.
- How to find out which Outbound Pool is used to send the emails?
- Cloud Only (Outbound emails sent from EXO).
- Cloud Only (Outbound emails sent from 3rd party email server).
- What is Criteria Based Routing (CBR).
- What is Centralized Mail Transport (CMT).
- Journaling in EXO.
- Conclusion.
Exchange Online Email Sending Pools.
EXO has few different set of servers that sends the email to the external recipients, and it depends on the content or quality of the email.
When a user sends an email, EOP outbound spam filters scans the email for outbound spam. If EOP detects spam, it sends the email to the external recipient server using a different email sending server (pool) than the normal one used for sending “high quality” email.
Different email sending pools have different set of IP addresses and purpose.
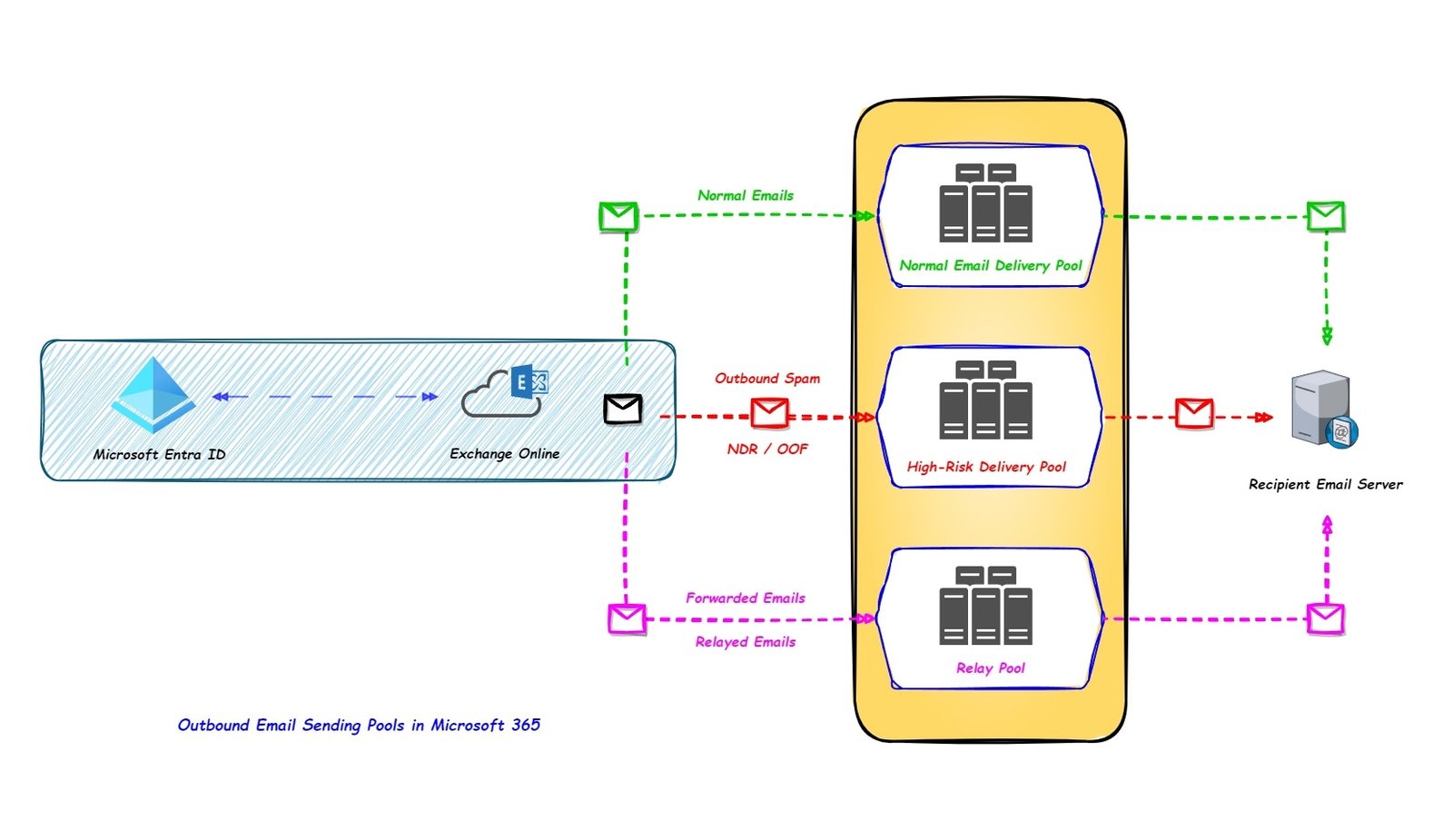
Normal Email Delivery Pool.
When the quality of the emails is high (no malicious or spam content) then the emails will be sent to the external recipient server using normal email delivery pool.
The normal email delivery pool has a good reputation of IP address and it is not blocked in the different Public Real Time Block Lists.
High-Risk Delivery Pool (HRDP).
The high risk delivery pool is a separate IP address pool for outbound email that’s only used to send “low quality” emails, Outbound emails that are detected as Spam, and lower-priority emails like Out of Office replies (OOF).
Non-delivery reports (also known as NDRs or bounce messages) are sent using HRDP servers.
If Microsoft sends out spam and NDR using normal email delivery pool, then there are chances that the normal email delivery pool IP address will appear on different third-party blocklists suspecting of sending spam messages.
Few email servers rejects the incoming SMTP connection request if the IP address of the server is listed in third-party blocklists.
Relay pool.
The emails that are forwarded or relayed using Microsoft 365 are sent from a special relay pool.
In these scenarios, the recipient server should not consider Microsoft 365 as the actual sender, Microsoft 365 is just forwarding or relaying the emails using Microsoft 365 servers.
The forwarded or relayed message should meet one of the following criteria to avoid using the relay pool:
- SPF passes when the message comes to Microsoft 365.
- DKIM on the sender domain passes when the message comes to Microsoft 365.
- The outbound sender is in an accepted domain.
At the time of writing this article, the Relay pool is using the IP address range 40.95.0.0/16
How to find out which Outbound Pool is used to send the emails?
We can use the below command to confirm if the outbound email is sent using Normal pool, HRDP or Relay pool.
PS C:\Users\ashutosh> Get-MessageTraceDetail -MessageTraceId a7******-****-4fe4-****-**********13 -RecipientAddress user@gmail.com | fl Message Trace ID : a7******-****-4fe4-****-**********13 Message ID : <PH***********************82@PH****39.nam***.prod.outlook.com> Date : 12-02-2024 07:01:41 Event : Send external Action : Detail : Message sent to gmail-smtp-in.l.google.com at 2607:****:****:***::1b using TLS1.2 with AES128 Data : *********;S:OutboundIpPool=1102;S:OutboundIpPoolName=RegularOutboundPool
- If S:OutboundIpPoolName=RegularOutboundPool then the email is sent using Normal Email Delivery Pool.
- If S:OutboundIpPoolName=HighRiskOutboundPool then the email is sent using High-Risk Delivery Pool.
- If the outbound server IP (is in the 40.95.0.0/16 range) then Relay Pool is used to send the email.
Cloud Only (Outbound emails sent from EXO).
This is a simple scenario, where the organization is using EXO to route the outbound email to the recipient email server. (no 3rd party email sending services are involved).

We have to make sure that the SPF, DKIM should be set to send the emails using EXO to avoid authentication failure at recipient email server.
The outbound mail flow would be like Sender –> EXO –> Recipient.
Cloud Only (Outbound emails sent from 3rd party email server).
If an organization does not want to use EOP to send the outbound emails then they can use the feature called Criteria Based Routing (CBR) and they can send all the outbound email to the 3rd party email gateway and then the emails are routed to the recipient email server.
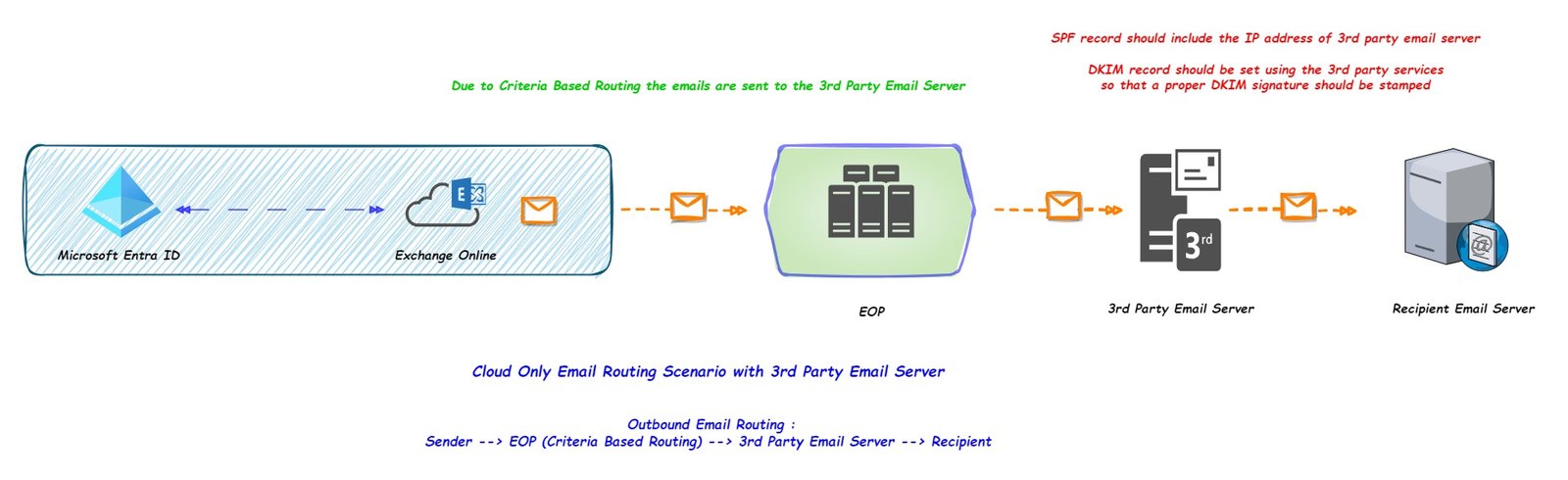
If an organization is using a 3rd party email server to send the email on the behalf of their domain then the SPF and DKIM record of the sender domain must include the IP address of the 3rd party email server and the 3rd party email services should help the organization to setup DKIM to send the email using their services.
What is Criteria Based Routing (CBR).
CBR is a method to change the default email routing, using CBR an organization can route the email to a specific outbound connector when the email matches a specific criteria.
In CBR, an organization has to first create an Outbound connector to route the email to a smart host or IP address, after that a transport rule is created with specific conditions and the action is set to use the outbound connector.
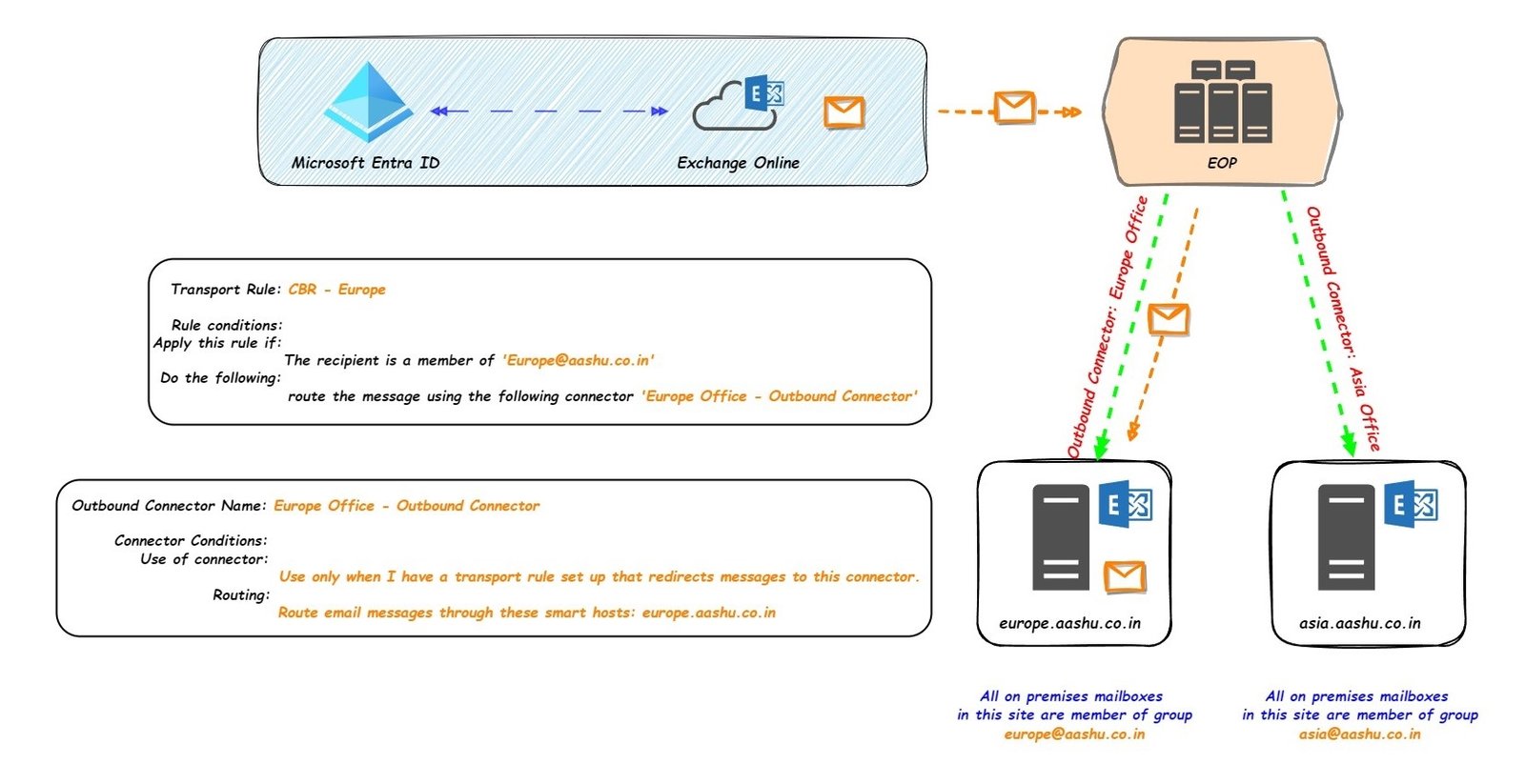
If an organization has 2 on premises sites, site is in Europe and site 2 is in Asia,
All the on premises mailboxes hosted on Europe site are member of a distribution group Europe@aashu.co.in , If a cloud mailbox wants to send email to the on premises mailbox (hosted on Europe site), then the sender just has to create an email, use the on premises mailbox email address in the TO field of the email and send it.
But in order for the email to route to on premises site, an Exchange Administrator had already created an outbound connector (Europe Office – Outbound Connector) and a transport rule (to route the email to connector ‘Europe Office – Outbound Connector’ if the recipient is a member of ‘Europe@aashu.co.in‘)
How to confirm if CBR is being used in an organization ?
We have to check the value of parameter IsTransportRuleScoped and Enabled for the outbound connector, if both the values are true that means the outbound connector is enabled and can be used in a transport rule to route the email using this connector
PS C:\Users\ashutosh> Get-OutboundConnector | fl Enabled,IsTransportRuleScoped
Enabled : True
IsTransportRuleScoped : TrueAfter that check if there is a transport rule which is routing the email to this connector and if it is enabled.
The transport rule would have the below conditions and action set.

What is Centralized Mail Transport (CMT).
Centralized Mail Transport is a configuration which allows organization to route mail from Exchange Online mailboxes through Exchange on-premises before delivering it to the intended recipient.
During the deployment of Exchange Hybrid using HCW, we will be provided with the option to enable Centralized Mail Transport.
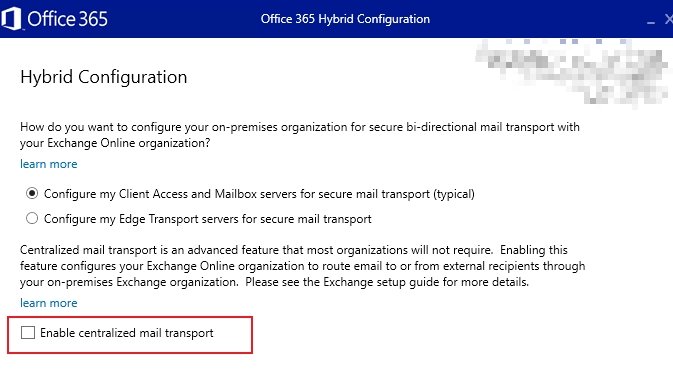
After an organization enables CMT, all the emails originating from a cloud mailbox that are sent to external users will be routed to on premises exchange server and then it will be routed to the external recipients.
Centralized mail transport is only recommended if organizations has a specific compliance-related transport needs to send external emails to on premises exchange server first and then route it to the recipient.
How to confirm if the CMT is enabled for an organization?
We have to check the output of the below command, if the value of RouteAllMessagesViaOnPremises is True then the CMT is enabled an the email will route to on premises exchange server set in the SmartHosts parameter of the outbound connector
PS C:\Users\ashutosh> Get-OutboundConnector | fl ConnectorType,SmartHosts,RouteAllMessagesViaOnPremises,CloudServicesMailEnabled
ConnectorType : OnPremises
SmartHosts : {mail.aashu.co.in}
RouteAllMessagesViaOnPremises : True
CloudServicesMailEnabled : TrueOutbound email routing when CMT is enabled.
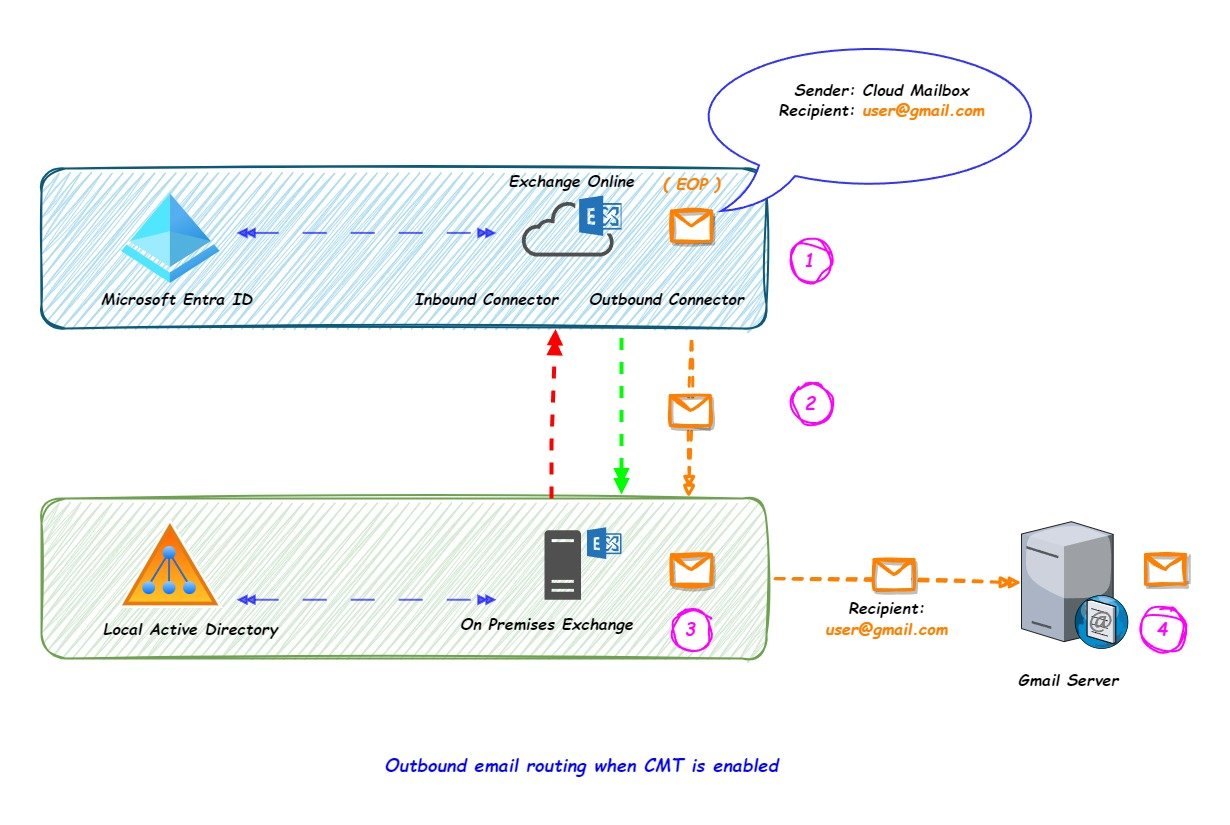
Consider a scenario where a mailbox hosted in cloud wants to send an email to Gmail user and CMT is enabled in the organization, then the routing would be as below
- Cloud Mailbox will compose an email with the recipient email address as user@gmail.com and send the email.
- Email reaches EOP and as the CMT is enabled the email will be sent to the on premises exchange server using outbound connector.
- The email is received by the on premises exchange server, process it for compliance (if a compliance solution is setup)
- The email is then sent to the external server (where the MX Record for the recipient domain is pointed)
The organization has to make sure that the SPF and DKIM record are set with respect to the on premises server as the external email will be sent using the on premises server.
Outbound email routing when CMT is disabled.
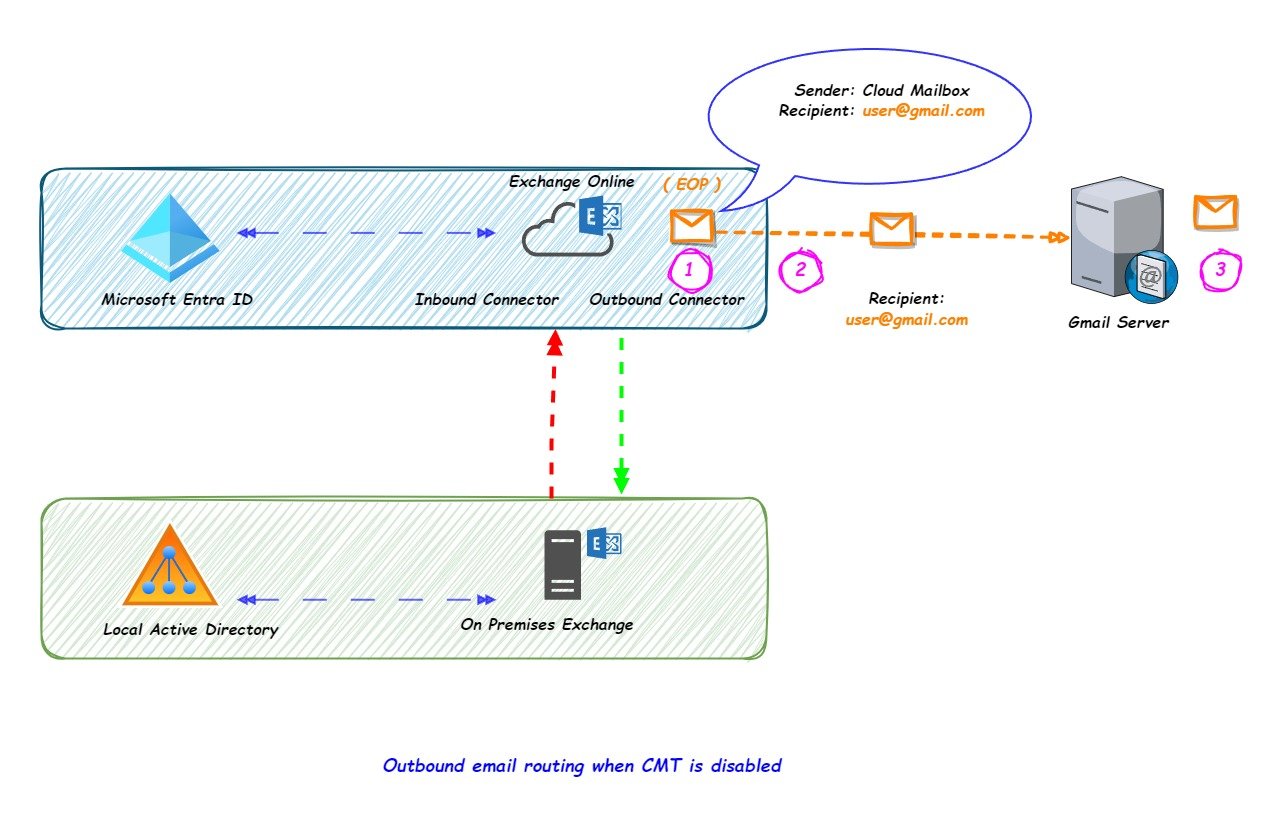
If a mailbox hosted in EXO wants to send an email to the Gmail user and CMT is disabled in the organization, then the outbound email flow will be as below
- EXO Mailbox will compose an email with the recipient email address as user@gmail.com and send the email.
- Email reaches EOP and EOP will check if CMT is enabled or disabled.
- As the CMT is disabled, the email will be sent to the Gmail server.
In this scenario, the SPF and DKIM records will be set with respect to Exchange Online.
Journaling in EXO.
Journaling is a company-wide email management strategy, using Journaling an organization can send the email copies (that are sent or received) to another mailbox (outside Exchange Online).
It is implemented as part of a legal or compliance regulation in the organization. In short, the email is copied from the mailbox into a dedicated mailbox for storing.
Journaling can be achieved in EXO by providing the below values.
- Journal rule scope: shows which emails should be journaled.
- Internal messages only: Journals the internal emails sent between the recipients inside your Exchange organization.
- External messages only: Journals the external emails sent to recipients or received from senders outside your Exchange organization.
- All messages: Journals all the emails that pass through your organization regardless of origin or destination.
- Journal recipient: shows the SMTP address of the recipient mailbox, all the copies of the journal emails will be sent to this email address. This should always be a mailbox which is not hosted in EXO.
More on Journaling in Exchange Online.
Journal email routing when CMT is disabled.
Once the journal rule is triggered, the journal email will be sent to the destination server using EOP.
Journal email routing when CMT is enabled.
As the CMT is enabled, the journal email will be sent to the on premises exchange server, where it will be processed and then the email will be sent to the destination email server.
Many organization has a specific requirement, use the features of CMT but use a different route for journaled emails (using EOP).
Organizations cannot be CBR in this scenario, as the journal emails are not controlled by Transport Rules.
Now the organization needs to create a second On Premises Outbound Connector with RouteAllMessagesViaOnPremises enabled to route journaled messages to the third-party journal system.
The outbound connector can be scoped by the RecipientDomains parameter to match the unique email domain or subdomain used by the journal mailbox.
PS C:\Users\ashutosh> Get-JournalRule | fl Name,JournalEmailAddress Name : Journal All Emails JournalEmailAddress : user@journal.abc.com
Now the Outbound connector should have the below values
PS C:\Users\ashutosh> Get-OutboundConnector | fl Name,ConnectorType,RecipientDomains,SmartHosts,RouteAllMessagesViaOnPremises
Name : Connector to Journal emails
ConnectorType : OnPremises
RecipientDomains : {journal.abc.com}
SmartHosts : {mail.journal.abc.com}
RouteAllMessagesViaOnPremises : True
Conclusion.
Outbound mail flow of the organization depends on the organization compliance requirement.
Routing the outbound email using EOP is simple configuration, while enabling CMT with hybrid is only suggested when the organization has a specific compliance requirement as CMT increases the mail flow complexity and also increases the email processing load on exchange on premises server as it has to process all the incoming emails from EOP and deliver those email to the internet.
An organization can also leverage CBR in order to change the email flow route in specific scenarios of mail flow. CBR uses the combination of outbound connector and transport rule to route the email to the specific destination server.